1. Technical background
1.1 Current situation of the aquaculture industry
Since the reform and opening up, the area of freshwater pond aquaculture in China has shown a rapid growth followed by a decline and then a trend of stabilization. The proportion of freshwater pond aquaculture area has been increasing year by year, from 26.51% to 52 15%; The production of pond aquaculture has been increasing year by year, with a relatively stable proportion of freshwater aquaculture production, increasing from 65.22% to 73.39%.
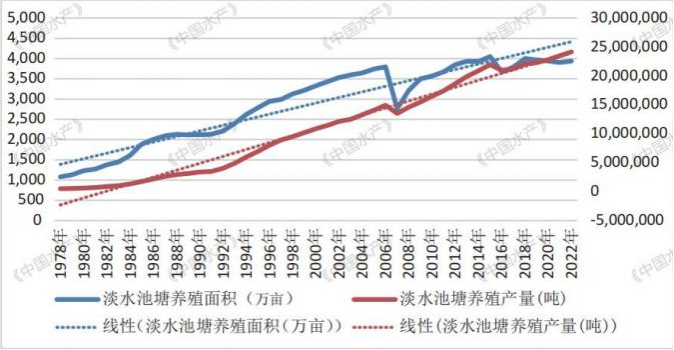
The area and yield of freshwater pond aquaculture in China from 1978 to 2022
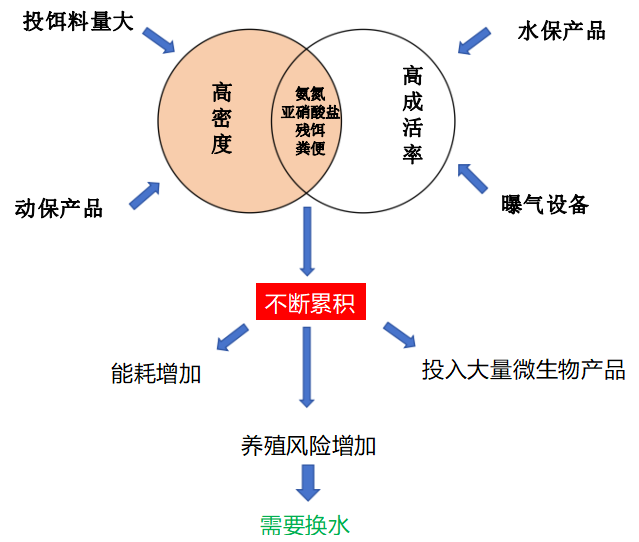
With the advancement of technology, the density of pond aquaculture has been increasing year by year, which means that the pollution level of aquaculture water is increasing day by day, and the discharge of its tail water is bound to cause a huge impact on the environment.
1.2 Formation and discharge characteristics of tailwater
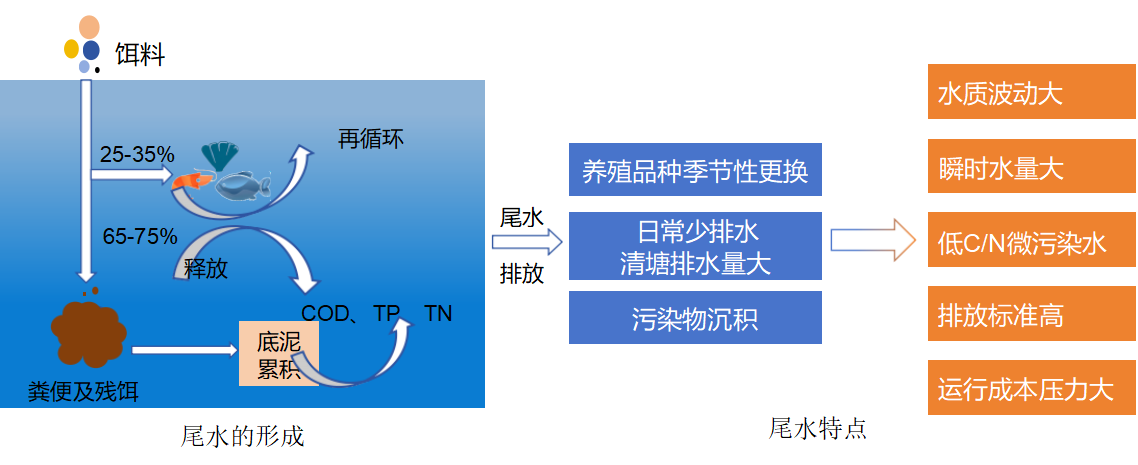
The pond aquaculture water contains substances such as excrement of aquatic animals, feed residues, and drug residues, which have accumulated over a long period of time, leading to the problem of exceeding various pollution indicators. The discharge of pond aquaculture wastewater has the characteristics of large water quality fluctuations, large instantaneous water volume, and high pollutant load. Random discharge will inevitably lead to water eutrophication, excessive cross-sectional water quality, and other hazards.
1.3. Policies for tail water discharge in the aquaculture industry
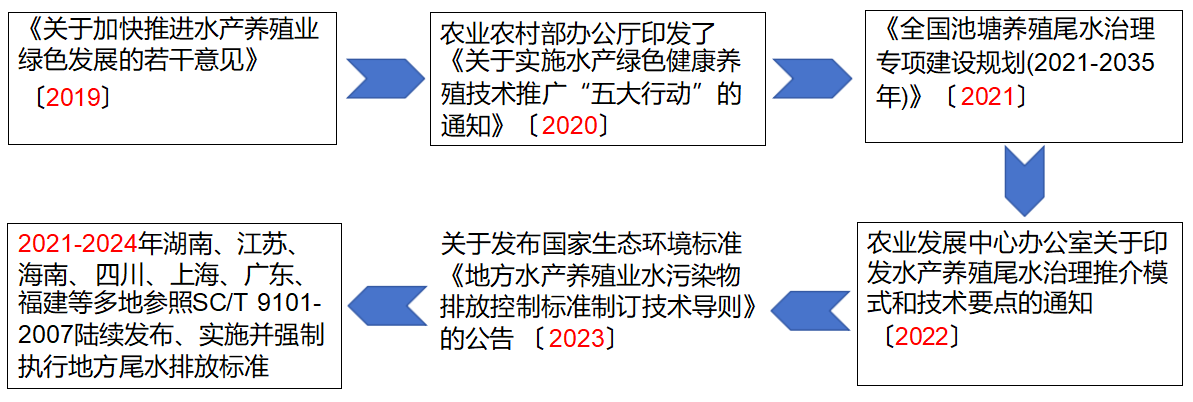
Guangdong released the DB44/2462-2024 Aquaculture Tail Water Discharge Standard in 2024, which will be implemented from May 1, 2024 and is a mandatory local standard.
Detailed policy guidance is imperative for tail water treatment!
1.4. Introduction to the traditional treatment process of three ponds and two dams for aquaculture wastewater
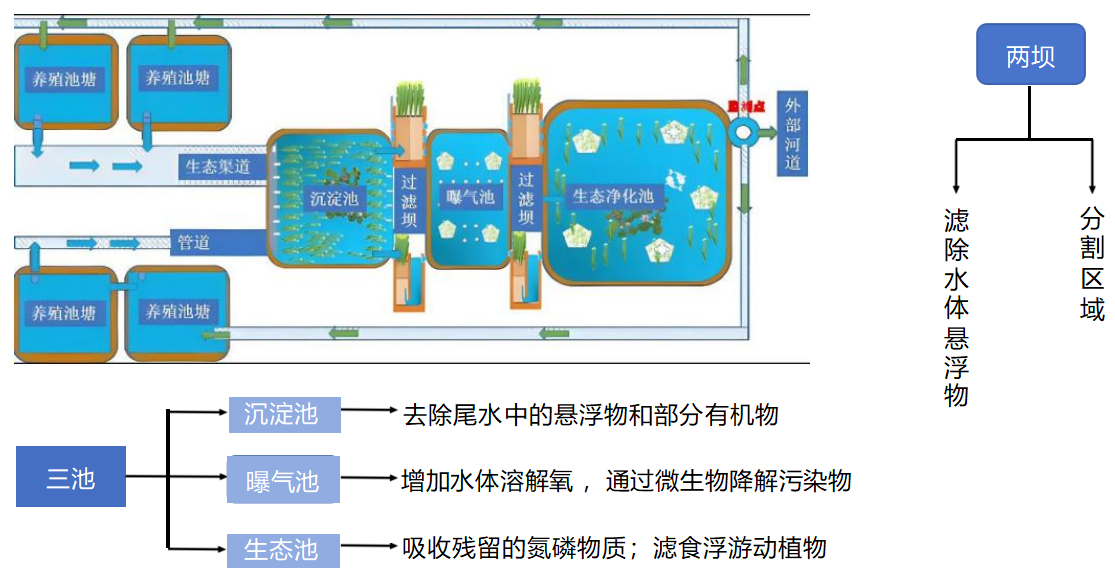
However, there are some limitations in the process of three ponds and two dams.
1.5. Limitations of the Three Ponds and Two Dams Process
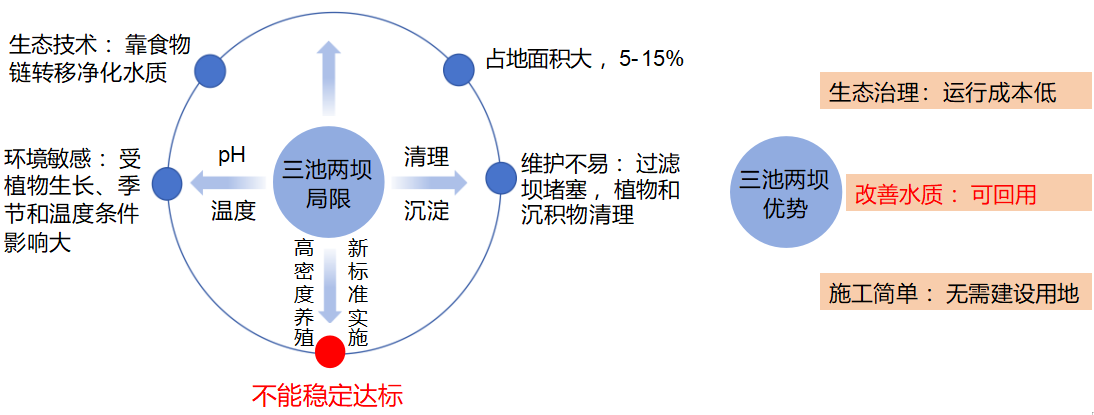
1.6. The dilemma of pond aquaculture itself
2. Technical roadmap
2.1. "Selective Enhancement and Two Water Synergy" Aquaculture Tail Water Treatment Technology
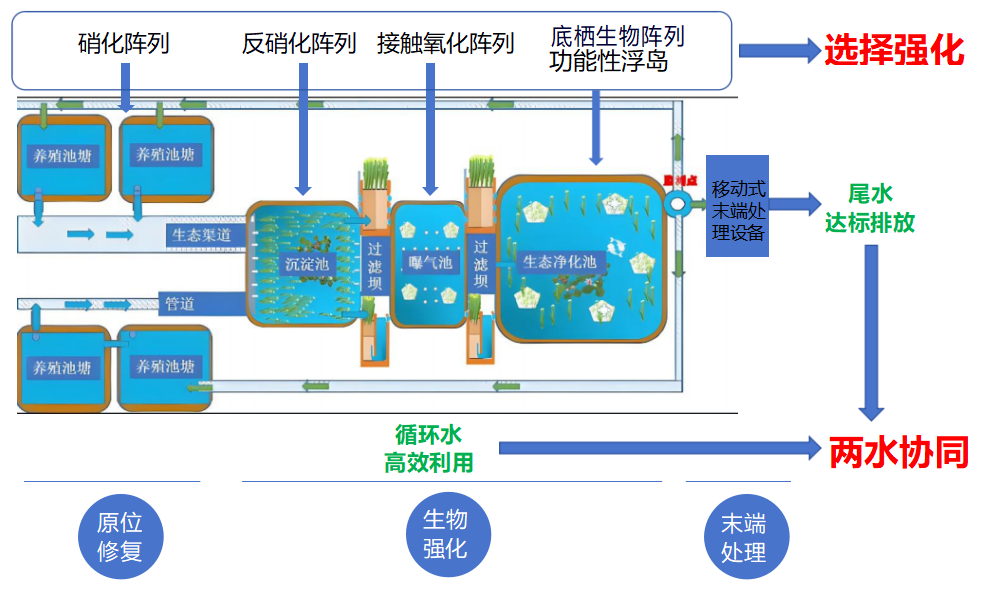
Selective enhancement refers to selective biological enhancement, which enriches specific functional microbial populations in ponds through specific culture media, such as nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria, heterotrophic aerobic bacteria, etc; Special functional powder materials that have adsorption effects on specific pollutants, promote growth, adsorption, and create a good environment for specific functional microbial populations, are loaded onto materials such as biological ropes, biological ribbons, and ecological porous sintered media to adsorb specific pollutants, forming a high concentration pollutant enrichment zone, thereby promoting the enrichment of specific functional microbial communities, and attaching specific microbial communities to the carrier surface, thereby efficiently removing pollutants. In the treatment of aquaculture wastewater, nitrifying biological ropes, denitrifying biological ropes, and nitrifying ecological porous media are mainly used to selectively enhance the biomass of functional microbial communities and pollutant removal efficiency in aquaculture ponds, three ponds, and two dams.
Two water synergy: Two water refers to the aquaculture tail water and pond circulating water. By selectively enhancing the biological removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen, TN, and COD in the pond and the three pond and two dam system, and utilizing the water purification function of the three pond and two dam system, the purified tail water is used as a water purification facility for aquaculture ponds in daily life. The purified tail water is directly reused. During the drainage season, it is used as a aquaculture tail water treatment facility, and with the cooperation of in-situ restoration of the pond and mobile sewage treatment equipment at the end, it meets the discharge standards. The Three Ponds and Two Dams system serves as both a circulating water purification facility and a tail water treatment facility, synergistically treating aquaculture tail water and pond circulating water. It not only solves the difficulties of pond aquaculture itself, but also achieves standard discharge of aquaculture tail water.
2.2. "Selective Strengthening and Two Water Synergy" Aquaculture Tail Water Treatment Technology
3. Core technology and core products
3.1 Principle of SFMC Technology
Selective Functional Microbial Community Construction (SFMC) Technology
Definition: A technology that specifically reduces specific pollutants in water through functional carriers and microorganisms.
Principle: By using the special components loaded on the carrier to adsorb pollutants, a high concentration pollutant enrichment zone is formed, and specific microbial communities are attached to the surface of the carrier, thereby efficiently removing pollutants.
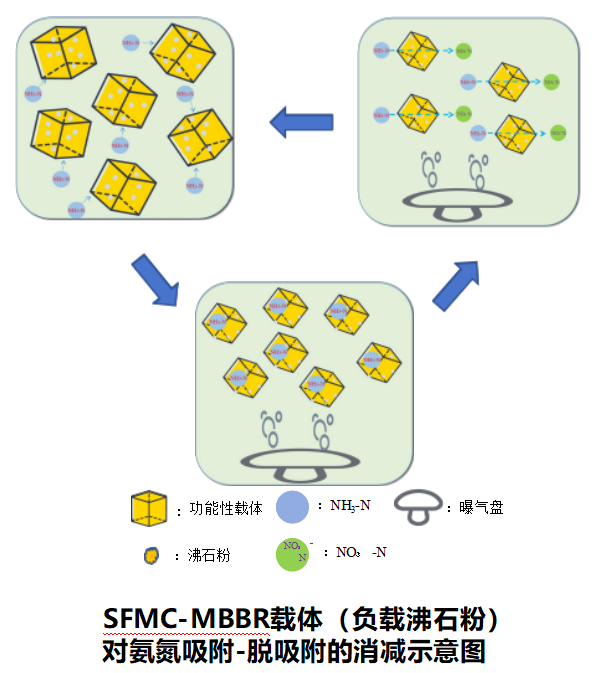
① Traditional carriers only provide a loading site for microorganisms and have no selectivity for functional microbial communities;
② The SFMC carrier creates a suitable growth environment for specific functional microbial communities through the modification of carrier structure and material properties, forming a unique microbial community on the carrier, greatly improving the degradation performance of immobilized microorganisms for specific pollutants and improving sewage treatment efficiency;
③ Compared to conventional carriers, SFMC carrier is a revolutionary leap that can greatly improve the efficiency of conventional pollutant treatment, break through the limit of bioreactor treatment capacity, and enable biological methods to treat difficult to degrade waste.
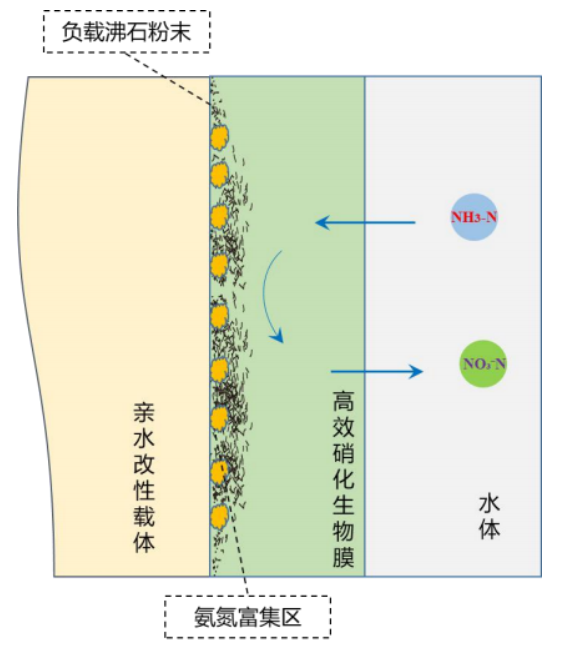
>Not only providing a microbial loading site, but also selectively targeting functional microbial communities.
>Not only does it provide a suitable environment for a certain functional microbial community, but it also provides a suitable environment for certain synergistic microbial communities. Through the synergistic effect of various microorganisms, the degradation of pollutants is completed, with selective microbial diversity.
>The combination of carriers and microorganisms not only relies on physical adsorption, but also on chemical bonds, which is particularly suitable for pre coating carriers and forming irreversible special microbial colonies, with irreversible microbial binding.
>The carrier has the function of enriching pollutants and can form local high concentration areas, which is conducive to the formation of corresponding microbial communities. Through adsorption and biological desorption, efficient removal of pollutants can be achieved.
>The carrier can break through the kinetic limit of the activated sludge method, reduce the k value, and decompose pollutants more thoroughly.

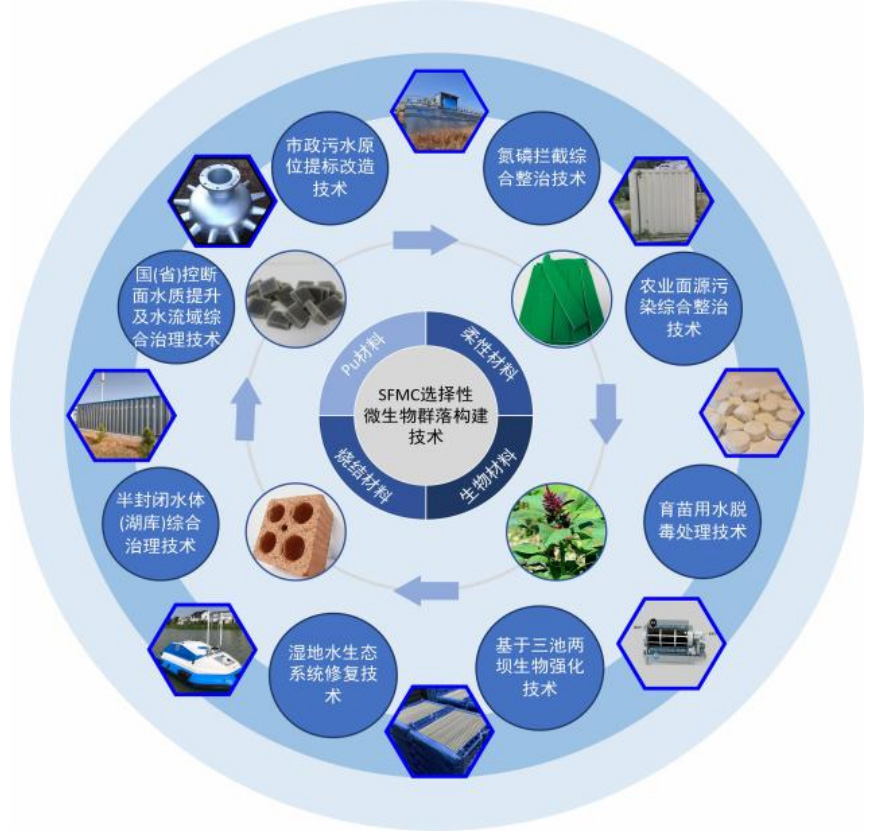
A Multi scenario Application Technology System for Collaborative Efficiency Enhancement of Wastewater Reduction and Carbon Reduction Based on SFMC
A series of functional materials and equipment have been developed based on SFMC technology:
>MBBR carrier
>Bioporous media
>Biological ribbons and ropes
>Plant fiber carrier materials
Applied to multiple fields:
>In situ upgrading and renovation of municipal sewage standards
>Comprehensive management of national/provincial control sections and clean small watersheds
>Agricultural and rural non-point source pollution control
>Treatment and recycling of aquaculture wastewater
>Lake and reservoir management and ecological wetland construction
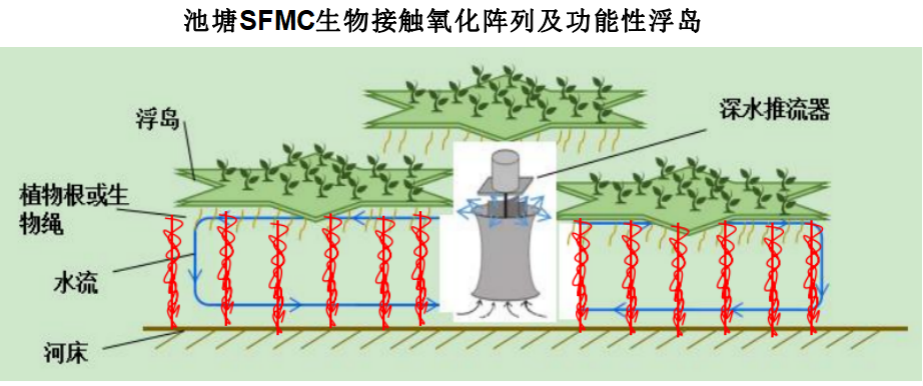
3.2 SFMC technology process
Using SFMC technology and flexible biological ropes as the basic architecture, functional powder materials are introduced into biological rope fiber materials. Combined with efficient nitrification bacteria enrichment and screening, biological quorum sensing and other technologies, SFMC biological fiber ropes with efficient nitrification function are constructed specifically for micro polluted water bodies; By using pond floats and supports, SFMC bio fiber ropes are directly suspended in the pond. Combined with the pond circulating thruster, a large-scale upper and lower layer circulating water flow is constructed to maintain sufficient mixing between the SFMC array area and other water bodies, improve reaction efficiency, and form efficient nitrification and denitrification SFMC contact oxidation arrays. These arrays are applied in fields such as lakes, reservoirs, grey water, aquaculture water, and aquaculture wastewater treatment.

① In situ restoration of ponds
In situ restoration of water withdrawal: After the completion of pond aquaculture, carbon sources and enriched indigenous denitrifying bacteria are added to the pond during the idle period. The circulating flow equipment in the pond is operated for 3-5 days, which can effectively reduce the total nitrogen and phosphorus content of the pond and provide conditions for the treatment of the tail water of the three ponds and two dams.
In situ remediation of aquaculture process: Adding 10-20% nitrification array to the pond can effectively treat ammonia nitrogen and nitrite during the aquaculture process, reduce aquaculture risks, improve aquaculture efficiency, and provide conditions for tail water treatment.
② End treatment of aquaculture wastewater
Due to the lack of stability in the ecological treatment process for tail water treatment, especially for TP indicators, there are no targeted treatment measures. Therefore, a set of mobile and efficient treatment equipment needs to be installed at the end of the third pond and second dam, which requires good phosphorus removal effect, small footprint, large water output, and mobility.


3.3 SFMC Technology Products

① Pond sediment oxidant
It can be directly sown in lakes or rivers, with simple construction and can be used under both water and waterless conditions.
The main ingredients of this product include functional microorganisms, co metabolic substrates, growth promoting agents, detoxifiers, special carriers, binders, sustained-release agents, etc. It can be made into various dosage forms such as powders, tablets, and pills according to on-site conditions.
The product not only reduces sediment, converts black and odorous sediment into "activated sludge", promotes microbial growth, inhibits the release of nutrients and organic pollutants in sediment, but also increases the redox potential of sediment, transforming it from anaerobic phosphorus release type to aerobic phosphorus absorption type, reducing total phosphorus in river and lake water, and achieving water quality purification.

② Pond circulating thruster
The pond circulation thruster adopts a guide tube and a pushing device to horizontally introduce the lower layer of water into the guide tube. The guide plate is pushed out around the upper layer of water, forming a horizontal circulating water flow centered on the vertical circulation thruster, with the upper layer of the pond water facing outward and the lower layer facing inward, to improve water purification efficiency.

③ End treatment equipment - mobile contact filter
By coupling micro flocculation technology with contact filtration technology, specific flocculants can be added to effectively convert dissolved and colloidal phosphorus into filterable micro flocs. These flocs are intercepted and removed in the subsequent filtration process, achieving efficient and rapid filtration of organic matter, suspended solids, and phosphorus removal.
4. Case analysis
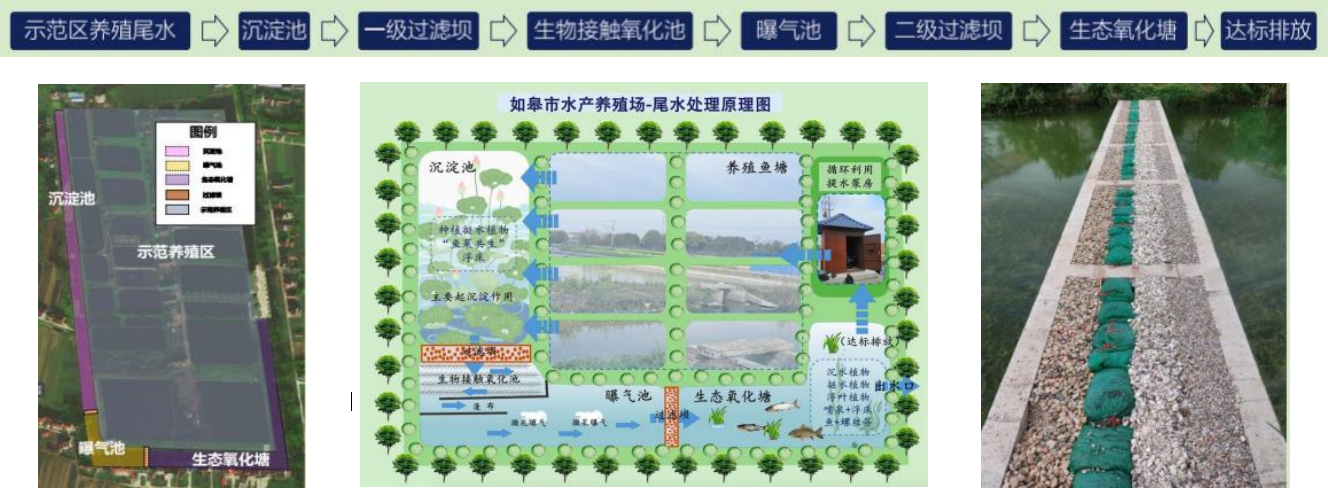
4.1. Freshwater aquaculture tail water treatment project at a certain aquaculture farm in Nantong, Jiangsu
Design concept: The governance system is a composite "four ponds and two dams" ecological treatment system, which adopts multifunctional combination and multi technology integration. It utilizes horizontal sedimentation tank process, biological contact oxidation process, enhanced aeration tank process, ecological purification pond process, "fish vegetable symbiosis" floating bed process, ecological filtration dam process, etc., to remove pollutants from the tail water in multiple ways and achieve the goal of deep treatment.
4.2. Tailwater treatment project in a township in Haikou, Hainan
Project Overview: The total treatment area of aquaculture wastewater in this project is 1200m2, with main pollutant contents of NH3-N3.6mg/L, COD 150mg/L, TP 9.2mg/L, and TN 4.65mg/L. The discharge of these pollutants has caused adverse phenomena such as water deterioration and ecological imbalance, seriously affecting the efficiency of aquaculture and the safety of aquatic products.
Design concept and governance effect: The project adopts a composite process system of "in-situ remediation+biological enhancement+end treatment", and reduces TN to below 2mg/L through SFMC denitrification array arranged in anaerobic denitrification tank; The coupling system of SFMC contact oxidation array and horizontal thruster is adopted in the biochemical tank to reduce COD to below 40mg/L and ammonia nitrogen to below 2mg/L; Use AFF micro flocculation equipment at the end to remove TP and SS. The combined effect of the three can effectively remove pollutants from the circulating water and tail water, stabilize the water quality of the circulating and tail water, and achieve the synergistic effect of recycling and reusing the aquaculture tail water or achieving standard discharge.

Post time: May-17-2024

